Applying Problem Based Learning (PBL)
What is Problem Based Learning (PBL)? Problem Based Learning (PBL) is a method in which learners are immersed in solving real-world problems. PBL is based…
What is Problem Based Learning and Why Should We Use It?
The term “Problem-Based Learning” (PBL) was originally developed by Barrows and Tamblyn (1980) for medical education. It is based on the Constructivist Theory of Learning.
PBL is a pedagogical strategy that uses open ended / ill-structured problems that mirror real-world problems. The authenticity of the problems helps students to transfer their knowledge and skills beyond the classroom, preparing them for the workplace and life in a rapidly changing world. The open ended nature of problems gives students the flexibility to approach it from different angles, to take different thematic sidelines according to their personal interests. This gives them control of the learning process, capturing their interest and motivating them to learn.
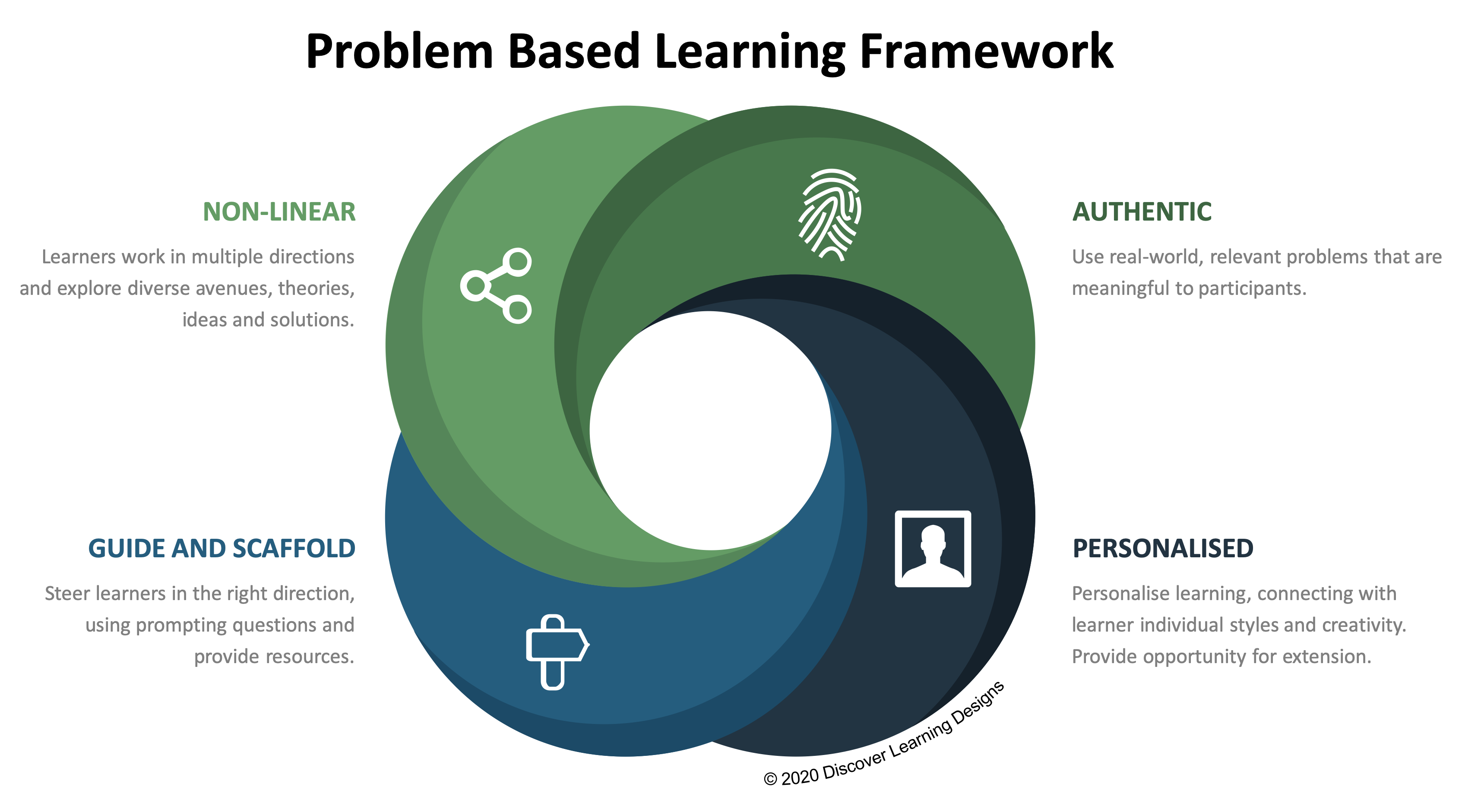
Lewis et al. (1998) emphasises that the act of posing problems is integral to the process of solving problems. Finding or posing problems is a creative endeavor that can occur prior to, during, or after the act of problem solving. By keeping the problem definition open, the students can “frame and reframe” their perspective on a problem so they reach “goal clarity”. Educational psychologists have discovered that solving a problem is a back-and-forth (recursive) process, not a linear one (Pea, 1985). In this way the student takes ownership of the problem thus enhancing their engagement and responsibility for the learning process.
“Teachers organise instruction around learning problems that pique student’s interest, challenge their current understandings, set the intended curricular concepts in meaningful contexts and allow students to explore ideas, pose interpretations or hypotheses, test their ideas, apply them in other contexts, and reflect on their learning.” (Jonassen et al., 2003, p 13)
Slavery and Duffy (1995) suggested the following principles of PBL:
Gudzial et al. (1997) consider the two most important aspects of problem based learning to be the authentic real world problems and students reflection on their experiences.
The teacher’s role changes from the provider of content to the facilitator of the learning process. Teachers present students with authentic problems and provide an environment where students can explore their ideas through research, discussion and reflection. The student has an active role identifying and locating resources, gathering and evaluating information.
Read more about Problem Based Learning (PBL) including how it incorporates many future required skills here.
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag(‘js’, new Date());
gtag(‘config’, ‘AW-960678877’);
Instructional Design: What is it?
Click on the links below to learn more about instructional design.
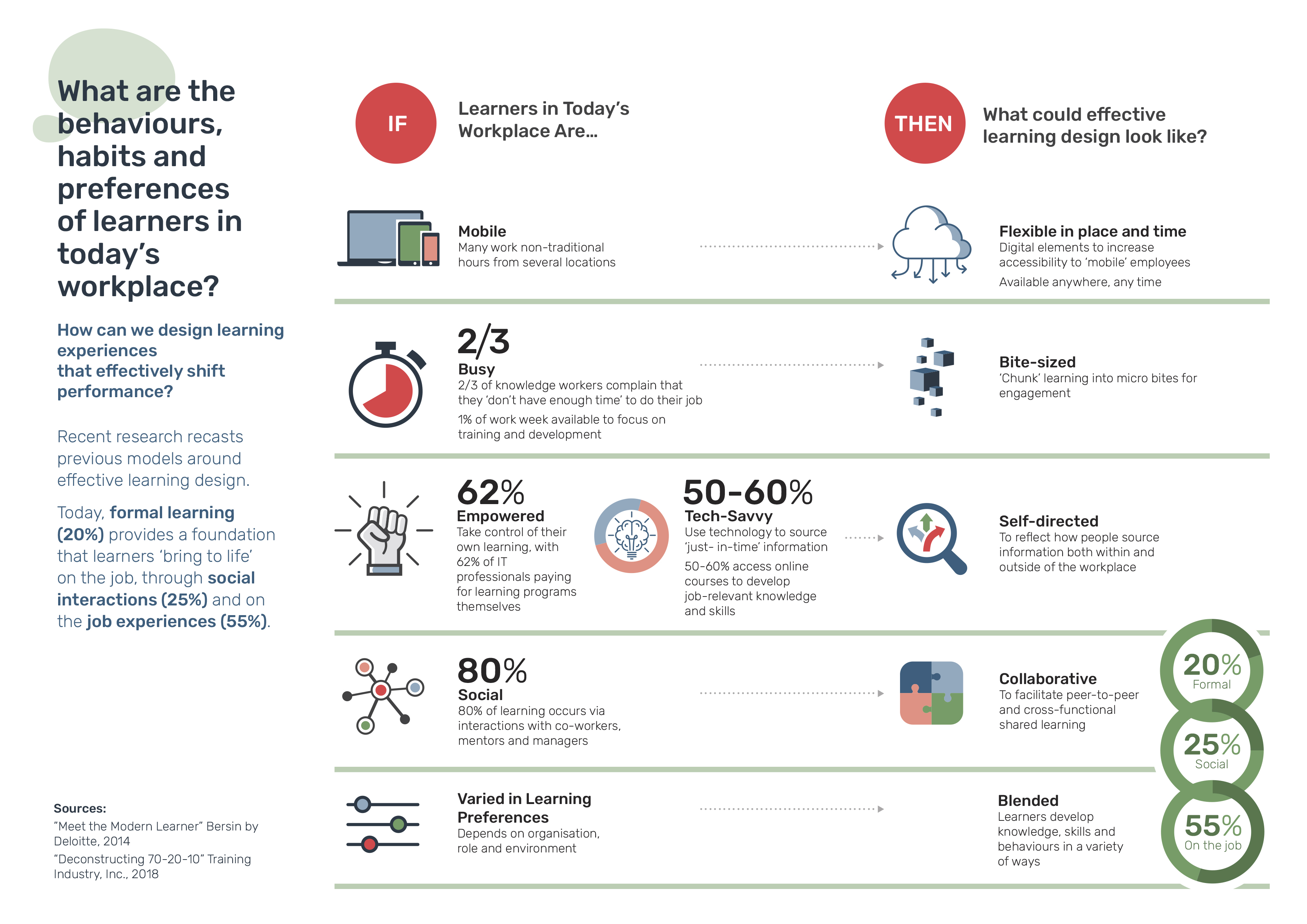
Influences On Learning Design In The Modern Workplace
Make An Enquiry
Office
E: info@discoverlearning.com.au
Ph: 1300 528 736
Michael Peart
E: michael@discoverlearning.com.au
Ph: 0434 075 231
Bianca Schimizzi
E: bianca@discoverlearning.com.au
Ph: 0416 013 623